Data Stores¶
Description |
Data repositories |
|---|---|
Projects |
39 |
Size vs. Trend Chart (click to view) |
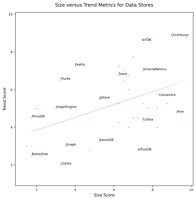
|
Sub-categories¶
Category |
Description |
Projects |
|---|---|---|
Data stores for running complex analytic queries. These typically provide SQL as a query language. |
4 |
|
These are data stores optimized to manage features, the input attributes for machine learning models. A feature store typically is layered on top of a lower level storage machanism, either a database, a key-value store, or cloud object storage. Features stores may also provide tools to create the feature values from the underlying data sources via an Extract Transform Load (ETL) process. |
4 |
|
Databases that manage data as a collection of nodes and edges between these nodes, rather than as tables with columns and rows. |
13 |
|
Data stores that store and retrieve data values based on unique keys. These store typically have simple query languages with operations to write a key/value pair query a value for a key, or query the values of a key range. Joins are typically not supported. |
5 |
|
Databases with a focus on event data with an associated timestamp, as seen in domains such as the Internet of Things or system monitoring. Such databases may have performance and storage optimizations for such data. They may use SQL, extensions of SQL, or specialized languages for their queries. |
13 |
